pix07
Well-known member
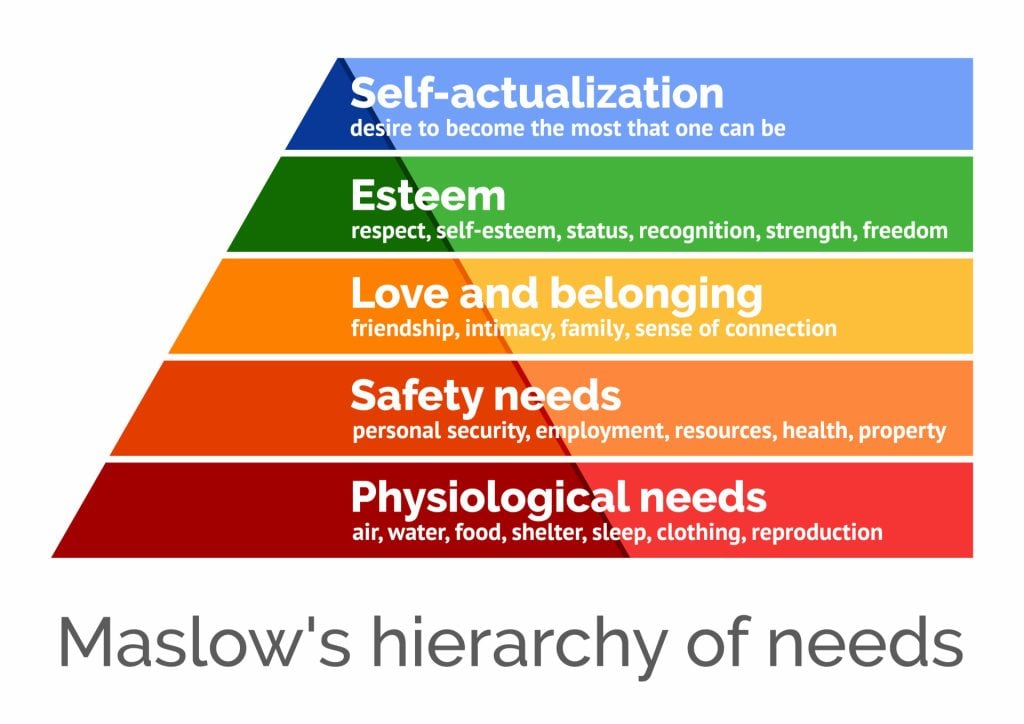
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is a motivational theory in psychology comprising a five-tier model of human needs, often depicted as hierarchical levels within a pyramid.
From the bottom of the hierarchy upwards, the needs are physiological (food and clothing), safety (job security), love and belonging needs (friendship), esteem, and self-actualization.
Needs lower down in the hierarchy must be satisfied before individuals can attend to higher needs.
Changes to the original five-stage model are highlighted and include a seven-stage model and an eight-stage model; both developed during the 1960s and 1970s.
- Biological and physiological needs – air, food, drink, shelter, warmth, sex, sleep, etc.
- Safety needs – protection from elements, security, order, law, stability, freedom from fear.
- Love and belongingness needs – friendship, intimacy, trust, and acceptance, receiving and giving affection and love. Affiliating, being part of a group (family, friends, work).
- Esteem needs – which Maslow classified into two categories: (i) esteem for oneself (dignity, achievement, mastery, independence) and (ii) the need to be accepted and valued by others (e.g., status, prestige).
- Self-actualization needs – realizing personal potential, self-fulfillment, seeking personal growth, and peak experiences.
Examples of transcendence needs include mystical experiences and certain experiences with nature, aesthetic experiences, sexual experiences, service to others, the pursuit of science, religious faith, etc.).
https://www.simplypsychology.org/maslow.html
